NFTs are omnipresent these days. Digital assets are selling for millions of dollars. What’s the deal with NFTs? Some analysts claim they’re a bubble; others think NFTs will revolutionize investment.
NFT. Definition
NFTs may be art, music, in-game stuff, films, etc. They’re sold online, often with bitcoin, and encoded using the same software as cryptos.
NFTs have been introduced since 2014, but nowadays, they’re growing in popularity as a tool to purchase and trade digital art. The NFT market was approximately $41 billion in 2021, nearing the global fine art market.
NFTs are one-of-a-kind or limited-run and contain unique identification codes. In contrast, most digital works are endless. Hypothetically, shutting off supply should boost the value of a demand-driven asset.
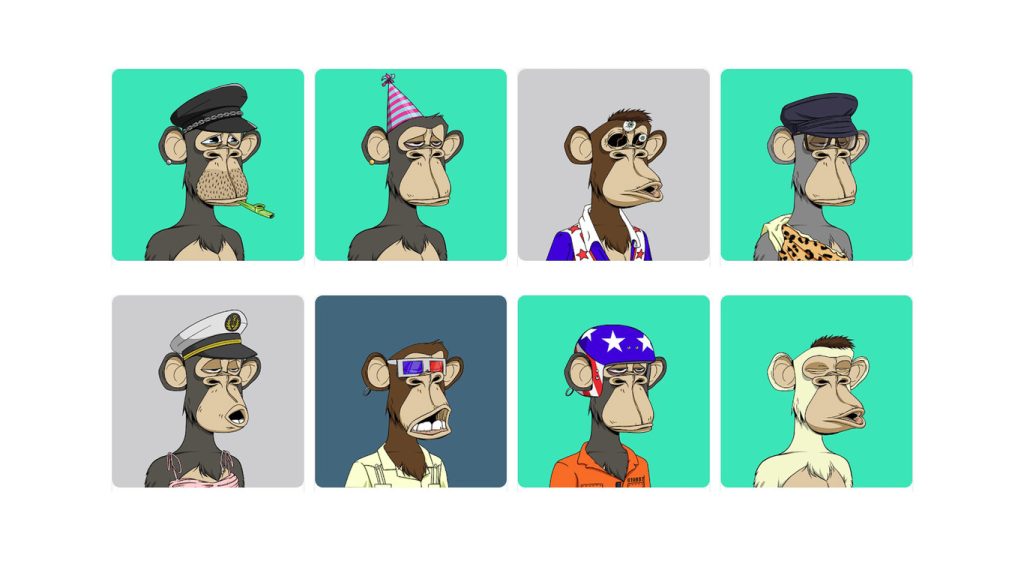
In the early days, many NFTs were digital works that already existed elsewhere, like NBA video clips or Instagram art. “EVERYDAYS: The First 5000 Days” by Mike Winklemann, or “Beeple,” sold at Christie’s for a record-breaking $69.3 million.
Anyone may see the photographs online for free. Why spend millions on something you can screenshot or download? Because NFTs let buyers keep the original item. It has built-in authentication to prove ownership. “Digital bragging rights” are nearly as valuable as the thing itself.

How Does It Work?
To show digital ownership, we need a transparent, immutable ledger that keeps track of all NFTs, who owns them, and where they point to.
Blockchain technology helps. By using blockchains’ publicly distributed, immutable nature, all NFTs may be kept transparently, enabling anybody to confirm their legitimacy at any moment.
Each time an NFT is exchanged or generated, the operation is permanently recorded on the blockchain and timestamped, so you can track any NFT back to its inception – helpful if you want to be sure your cartoon monkey or virtual kitten is real.
Why Are NFTs Important?
Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) have transformed gaming and collectibles for crypto consumers and enterprises. Since June 2017, $25 billion, including $21 billion in secondary sales, has been spent on NFTs.
NFTs allow players and collectors to become immutable owners of in-game objects and other unique assets, as well as develop and commercialize virtual casinos and theme parks.
All sorts of player-created items, like outfits, avatars, and virtual currency, may be traded and sold between players on the secondary market. Artists may retain a larger share of their sales proceeds by selling digital artwork directly to a worldwide audience without employing an auction house or gallery. Digital artwork may be configured to pay royalties to the artist when it’s sold.
William Shatner, “Star Trek’s” Captain Kirk, distributed 90,000 digital cards of himself on the WAX blockchain in 2020. Shatner earns a royalty every time a $1 card is resold.
NFTs Are Valuable Because…
Supply and demand determine pricing for all assets. Due to their scarcity and strong demand from players, collectors, and investors, NFTs are typically expensive.
Some NFTs may be quite profitable. One player on Decentraland combined 64 parcels into a single estate. It sold for $80,000 due to its position and road access.
Another investor spent $222,000 on a digital Monaco track in F1 Delta Time. The NFT representing the digital track gives the owner 5% of all race entrance fees and dividends.
Costliest NFTs
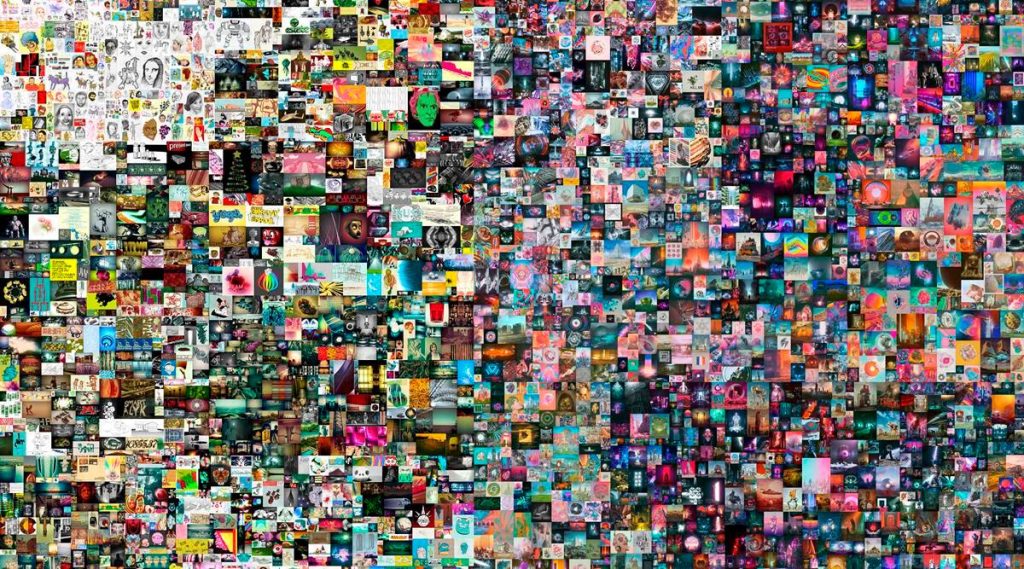
In December 2021, 312,686 pieces of a fractionalized NFT artwork named “The Merge” were auctioned for $91.8 million. Second place goes to Beeple’s Everydays: The First 5,000 Days, which sold for $69.3 million.
10,000 people formed an “AssangeDAO” to buy “Clock” for $52.7 million. This is a timer that tracks Julian Assange’s incarceration time. Assange established it alongside digital artist Pak to collect money for his legal battle.

How is NFT Different from Crypto?
A non-fungible token uses the same code as Bitcoin or Ethereum, but that’s it. Physical money and cryptocurrency may be bought and swapped. One dollar equals another dollar; one Bitcoin equals another Bitcoin. Crypto’s fungibility makes it a credible blockchain currency. NFTs vary. Each NFT has a digital signature that prevents exchange or equivalence (hence, non-fungible).
NFTs can’t be traded on controlled or decentralized exchanges, unlike other cryptocurrencies. To list and trade these assets, users must utilize NFT markets. OpenSea and Rarible are popular, but there are numerous additional possibilities.
Buying NFTs
To store NFTs and cryptocurrencies, you’ll need a digital wallet. Depending on your NFT provider, you may need to buy Ether. Coinbase, Kraken, PayPal, and Robinhood all accept credit cards. Then you may transfer it to your wallet.
When researching choices, consider fees. When buying crypto, most exchanges charge a percentage.
NFT Marketplaces
Once your wallet is set up and financed, NFT sites abound. NFT markets include:
OpenSea.io: It sells rare digital objects and treasures. To see NFT collections, establish an account. Discover new artists by sorting by sales volume.
Rarible: Like OpenSea, Rarible is a democratic, open marketplace for NFTs. RARI token holders may vote on fees and community regulations.
Foundation: Artists must earn “upvotes” or invitations to upload work. The community’s exclusivity and expense of entry—artists must buy “gas” to mint NFTs—may result in higher-quality art. Chris Torres (Nyan Cat creator) sold the NFT on Foundation. It may also imply higher pricing, which isn’t always a bad thing for artists and collectors looking to profit if NFT demand maintains steady or rises.
Although these marketplaces house thousands of NFT makers and collectors, do your research before purchasing. Impersonators have sold some artists’ work without authorization.
Some platforms have stricter creator and NFT verification requirements than others. OpenSea and Rarible don’t verify NFT ownership. When buying for NFTs, keep the ancient adage “caveat emptor” in mind.







[…] of providing them with a means of digitizing their work. Each of these works will be issued as a non-fungible token (NFT), which means that its owner will have exclusive rights to it and can be sure that it is a […]
[…] Prime Minister Fumio Kushida made an announcement favoring NFTs, the Metaverse, and the Web3 sector as a whole at the beginning of October. Prime Minister Kushida […]